Critical Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Identified in OpenKM Document Management System | Terra System Labs
What is OpenKM
Enterprise Document Management Systems (DMS) form the backbone of modern organizational operations. From internal business records and intellectual property to government files and compliance documentation, these platforms are trusted to securely store and manage some of the most sensitive digital assets an organization owns.
During recent security research, Terra System Labs identified multiple critical zero-day vulnerabilities in OpenKM, a widely deployed Document Management System with over 6 million downloads worldwide. OpenKM is actively used by MSMEs as well as government organizations across multiple countries, and is available in both open-source and enterprise editions.
Given the scale of adoption and the critical nature of the data handled by OpenKM, the security impact of these findings is significant.
Scope of the Discovery
The vulnerabilities were identified and validated as part of controlled security research conducted in isolated lab environments, following strict ethical guidelines. No production systems, customer environments, or third-party infrastructure were accessed during the research.
The identified issues affect core application logic and backend workflows, making them particularly dangerous. Unlike simple configuration issues, these vulnerabilities arise from how the application processes requests, handles authorization, and interacts with underlying system components.
Summary of Identified Vulnerabilities
Terra System Labs identified the following critical vulnerability classes in OpenKM:
1. Local File Inclusion (LFI)
The application contains file-handling logic that, under specific conditions, may allow an attacker to access internal server files that were never intended to be exposed.
If abused, this vulnerability could allow attackers to:
-
Access sensitive configuration files
-
Retrieve application secrets and credentials
-
Gain deeper insight into system architecture
LFI vulnerabilities are often used as an initial foothold, enabling attackers to escalate privileges or chain further attacks.
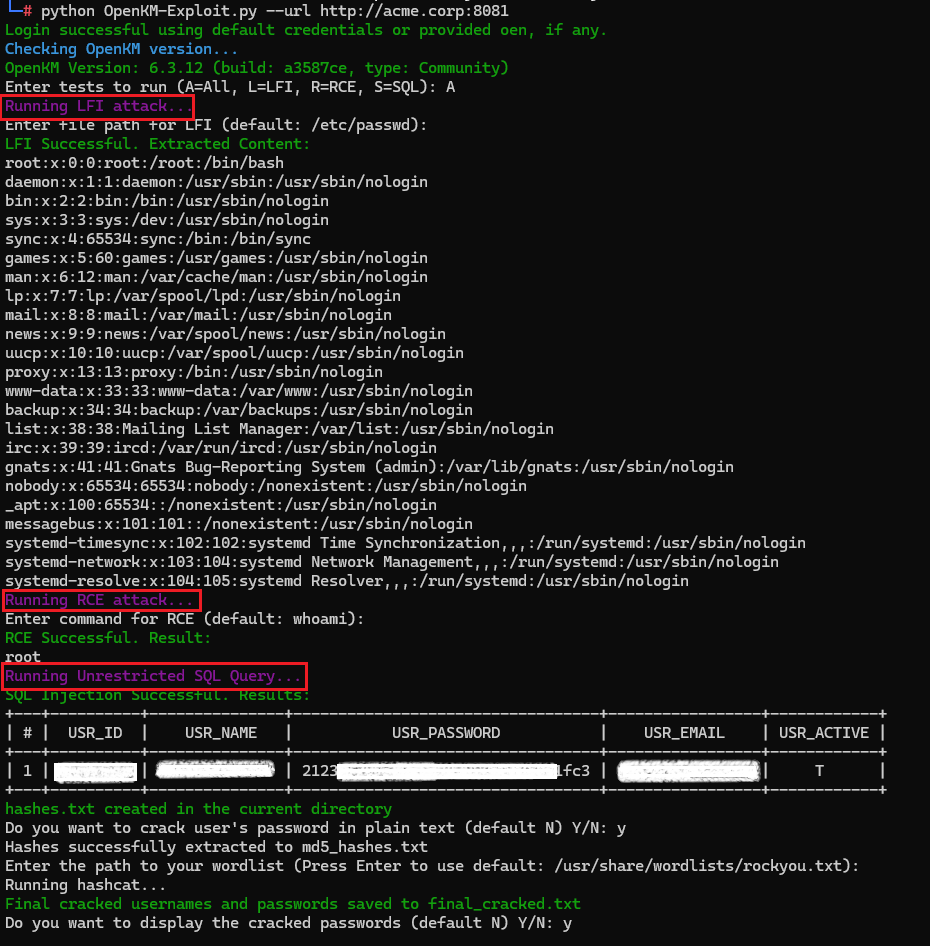
2. Unrestricted SQL Command Execution
The research also identified backend database interaction paths that lack sufficient authorization enforcement. In certain scenarios, this could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary SQL commands against the application database.
Potential consequences include:
-
Disclosure of sensitive metadata and user information
-
Manipulation or deletion of stored data
-
Credential harvesting for further compromise
Database-level access dramatically increases attacker capabilities and often acts as a stepping stone toward full system takeover.
3. Remote Code Execution (RCE)
The most severe finding involves the potential for Remote Code Execution (RCE). Under specific conditions, an attacker may be able to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying server hosting OpenKM.
RCE vulnerabilities are considered high-impact by design, as they allow attackers to:
-
Take full control of the application server
-
Deploy malware or persistent backdoors
-
Pivot into internal networks and adjacent systems
Chained Exploitation and Advanced Attack Scenarios
While each vulnerability is critical on its own, the real risk emerges when they are chained together.
In a realistic attack scenario:
-
An attacker may use LFI to gather internal configuration details
-
Leverage SQL command execution to escalate privileges or harvest credentials
-
Achieve RCE, resulting in full server compromise
Once control is established, attackers can perform lateral movement, targeting:
-
Internal databases
-
File servers
-
Identity systems
-
Other trusted internal applications
This transforms a single application flaw into an enterprise-wide security incident.
Impact on MSMEs and Government Organizations
OpenKM is widely adopted by MSMEs and government entities, many of which operate in regulated or resource-constrained environments. These organizations often rely on OpenKM as a trusted internal system, assuming that perimeter controls alone are sufficient.
Zero-day vulnerabilities in such platforms introduce serious risks:
-
Exposure of confidential or classified data
-
Compliance failures (ISO 27001, GDPR, SOC, local regulations)
-
Operational disruption
-
Legal and reputational damage
For government deployments, the risk may extend to national data protection obligations and public trust.
Responsible Disclosure and Advance Notification
As a responsible security research organization, Terra System Labs has taken proactive steps to minimize real-world risk.
Actions taken include:
-
Privately reaching out to affected organizations using OpenKM
-
Providing advance notice of the vulnerabilities
-
Sharing high-level remediation guidance
-
Offering support for validation and secure configuration
Public disclosure of technical exploitation details has been intentionally delayed to give organizations adequate time to assess and secure their environments.
Why High-Level Disclosure First
Immediate publication of exploit-level details for zero-day vulnerabilities in widely used enterprise platforms can significantly increase the likelihood of real-world exploitation.
For this reason, Terra System Labs is publishing:
-
A high-level advisory now
-
A full technical disclosure at a later date
This approach balances transparency with responsibility, prioritizing defensive readiness over sensational exposure.
Upcoming Technical Disclosure
📅 Scheduled for release on Friday 16 Jan 2026, the upcoming technical publication will include:
-
In-depth vulnerability analysis
-
Conceptual exploitation paths (without weaponization)
-
Nuclei detection templates for defensive validation
-
Python-based proof-of-concept code for authorized testing
-
Mitigation, hardening, and monitoring recommendations
Until that release, specific endpoints, request parameters, payloads, and exploit chains remain undisclosed.
Immediate Recommendations for OpenKM Users
Organizations currently using OpenKM should consider the following immediate actions:
-
Audit the OpenKM deployment
-
Restrict management interfaces to trusted networks
-
Enable detailed logging across application, database, and OS layers
-
Conduct a focused Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Test (VAPT)
Proactive assessment can significantly reduce the attack surface before exploit details become public.
PoC:
Nuclei template to Remote Code Execution (RCE) on the OpenKM deployment server.
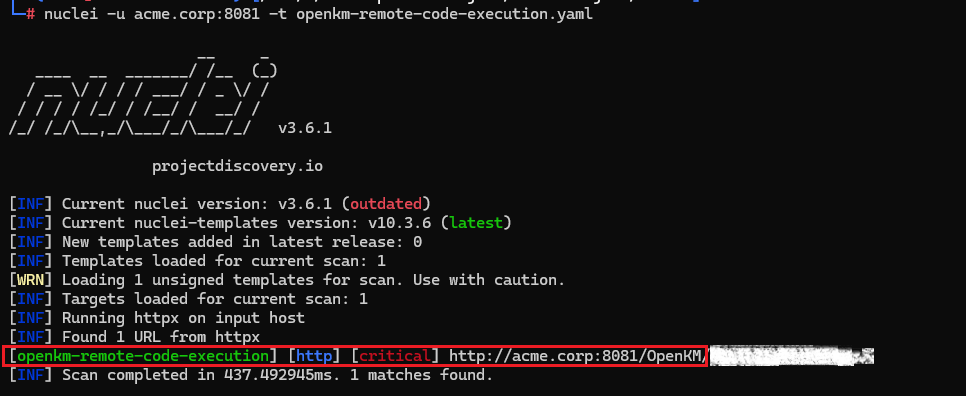
Nuclei template to Local File Inclusion (LFI) on the OpenKM deployment server.
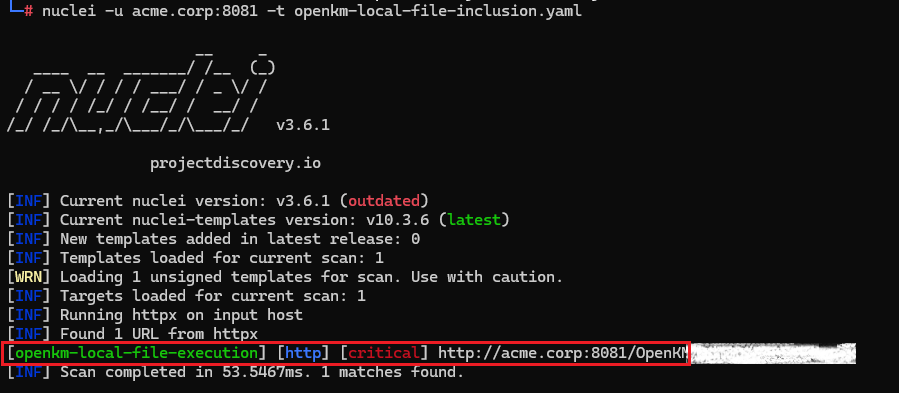
Nuclei template to Database Query Execution on the OpenKM deployment server.

OpenKM Exploit suite to exploit all the above vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
OpenKM’s widespread adoption across MSMEs and government organizations worldwide makes these zero-day vulnerabilities particularly impactful.
This research demonstrates that:
-
Even mature and widely trusted platforms require continuous security evaluation
-
Internal applications are not immune to zero-day threats
-
Responsible disclosure plays a critical role in reducing ecosystem risk
Terra System Labs remains committed to ethical security research, responsible disclosure, and helping organizations strengthen their security posture before attackers exploit these gaps.
📢 The detailed technical disclosure will be published on Friday 16 Jan 2026 .
About Terra System Labs
Terra System Labs is a cybersecurity research and consulting firm specializing in Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing (VAPT), Application Security, and Advanced Threat Research, helping enterprises and public-sector organizations identify and remediate critical security risks before they are exploited.
Recent Posts